- Why graph signal processing?
- What is graph in DSP?
- How is graph a signal?
- What is meant by signal processing?
Why graph signal processing?
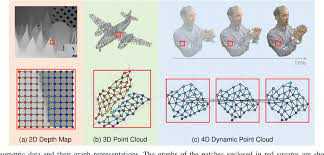
Graph Signal Processing provides a new perspective for network data processing and its theoretical tools, such as Graph Fourier transform, graph sampling, reconstruction, graph filter, and graph wavelet.
What is graph in DSP?
A DSP program is often represented using a DFG, which is a directed graph (i.e., each edge has a distinct direction) that describes the program (see also Section 1.4. 3). For example, the program y(n) = ay(n − 1) + x(n) is graphically represented in Fig. 2.1(a). A simplified version of this program is shown in Fig.
How is graph a signal?
Formal Definition of Graph Signal
We can represent a graph G as a set of vertices V, edges E, and a weight matrix W as follows. Edges can have different weights and weight matrix will store these values. Let the cardinality of V to be N (|V| = N). This means that there are N vertices in our graph.
What is meant by signal processing?
Signal processing involves converting or transforming data in a way that allows us to see things in it that are not possible via direct observation. Signal processing allows engineers and scientists to analyze, optimize, and correct signals, including scientific data, audio streams, images, and video.
 Howtosignalprocessing
Howtosignalprocessing